High Cholesterol: lipid-related metabolic changes, known as dyslipidemias and involving [high cholesterol] or triglycerides, along with hypertension, diabetes, and smoking, are among the main predisposing factors for cardiovascular disease. High cholesterol or hypercholesterolemia has the greatest effect in this group, increasing their presence. Besides, In the Basque Country, its estimated that 20% of the population over 18 years of age and 40% of patients in outpatient clinics experience some change of this type.
Although [high cholesterol] is not a short-term problem, if maintained for a long time, it accelerates the development of arteriosclerosis, an age-related degenerative process of the arteries. The accumulation of fatty deposits causes the narrowing and hardening of the ducts. Blood flows to the organs, which can completely block them with serious consequences for the heart (heart attacks) and the brain (stroke, stroke).
Genetic factors contribute to an increase in so-called bad cholesterol, although it affects by environmental factors and certain habits. They can increase this risk:
- Age
- being overweight – although thin people should also watch their cholesterol
- physical inactivity
- improper diet.
On other occasions, dyslipidemia caused by liver, endocrine, and kidney diseases or by taking certain drugs.
Table of Contents
What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a lipid. It is a waxy, fat-like substance that the liver produces naturally. It is vital for the formation of cell membranes, certain hormones, and vitamin D.
It does not run in water. and, so it cannot pass through the blood on its own. To help transport cholesterol, your liver makes lipoproteins.
Lipoproteins atoms made up of fat and protein. And, they carry cholesterol and triglycerides (another type of lipid) through the bloodstream. The two central forms of lipoproteins are low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
What Are The Symptoms Of High Cholesterol?
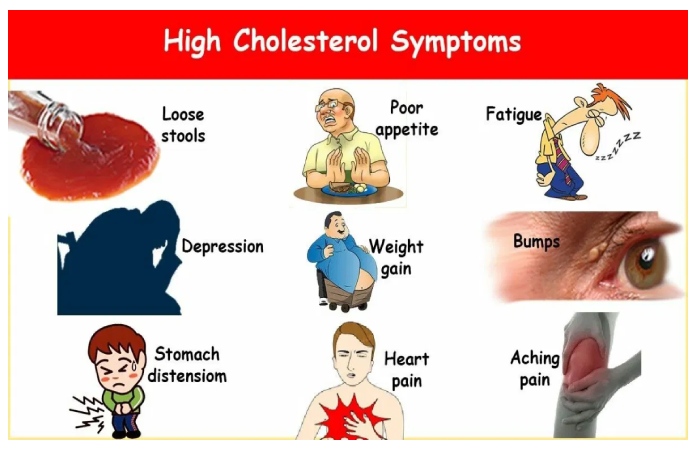
Despite the belief that hypercholesterolemia causes headaches or dizziness. It doesn’t cause any symptoms, increasing its danger. Also, To avoid it from occurring in people at risk for coronary heart disease, a series of tests, known as lipid profiles, are recommended between 35 and 40. Medical control should be carried out periodically, depending on the presence or absence of other risk factors and the circulatory system’s presence of diseases.
How To Prevent High Cholesterol?
Preventing and treating it requires a lifestyle change: healthy eating, reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, avoiding excess weight, and exercising. All are necessary measures. But what is the real key? Food for sure. A balanced and varied diet should prioritize the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and fish to the detriment of fats, limiting them to 25-30% with a greater presence of unsaturated -vegetables- versus saturated of animal origin. Besides, in the case of hypercholesterolemia, And, the latter should not represent more than 7% in the diet.
Do Functional Foods Lower High Cholesterol?

Currently, a large number of functional foods and nutritional supplements advertised, as beneficial for these diseases. Phytosterols and ethanol. Molecules with a structure similar to the vegetable kingdom and block intestinal absorption. Therefore, they are naturally present in corn, sunflower, and soybean oil. To a lesser extent, fresh vegetables, and fruits. Consuming 1 to 2 grams per day lowers cholesterol levels. It is marketed in various foods, especially fortified dairy products. Although prophylactic use is not recommended for normal cholesterol people.






