Table of Contents
What is Diabetes
Diabetes is a non-transmissible long-term condition; it develops slowly but does not spread from person to person by physical contact.This is the body’s inability to manage blood sugar levels. Insulin generated in the pancreas is the hormone responsible for regulating and transforming sugar into energy.
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) develops when a child’s body’s insulin synthesis is impaired, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. This illness can lead to issues in the heart, lungs, eyes, and kidneys, liver, as well as an increased risk of infection.
We wish to protect our children from illness and sickness as much as possible. Diabetes has an impact on how the body uses glucose. Although some children are unable to avoid type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes can be avoided, and there are numerous techniques to do so.
Type 1 Diabetes
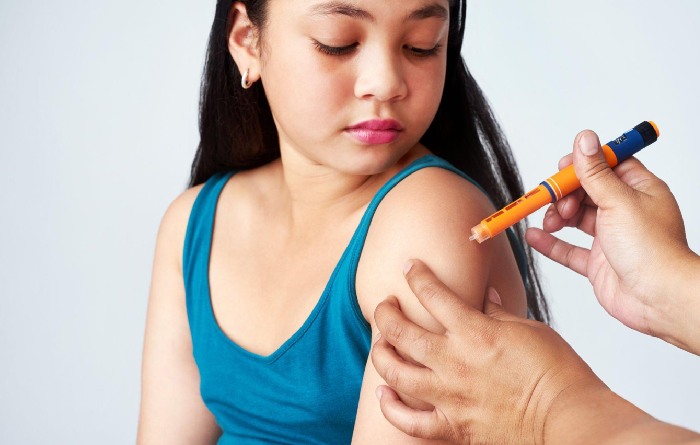
No one knows for sure what reasons type 1 diabetes, but scientists believe that it’s a genetic order or that a child must have been exposed to something else to get this disease. Type 1 diabetes isn’t contagious, so your child can’t get it from another person or pass it along to anyone.
Although type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, you can manage it. Conferring to the American Diabetes Association or ADA that breastfed babies have a lower risk of developing type 1 diabetes and becoming overweight or obese later in life, which is also a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. You can also manage type 1 diabetes by avoiding feeding them solid foods at a very young age. There are other things you can do to manage type 1 diabetes:
- Lessen foods that are high in fats and properly portion your carbs. If you include carbohydrates in your family diet, make sure that you incorporate other foods that include the important nutrients that your child will need.
- Learn about the different medications and consult a health professional about your child’s medication and what best fits his/her need.
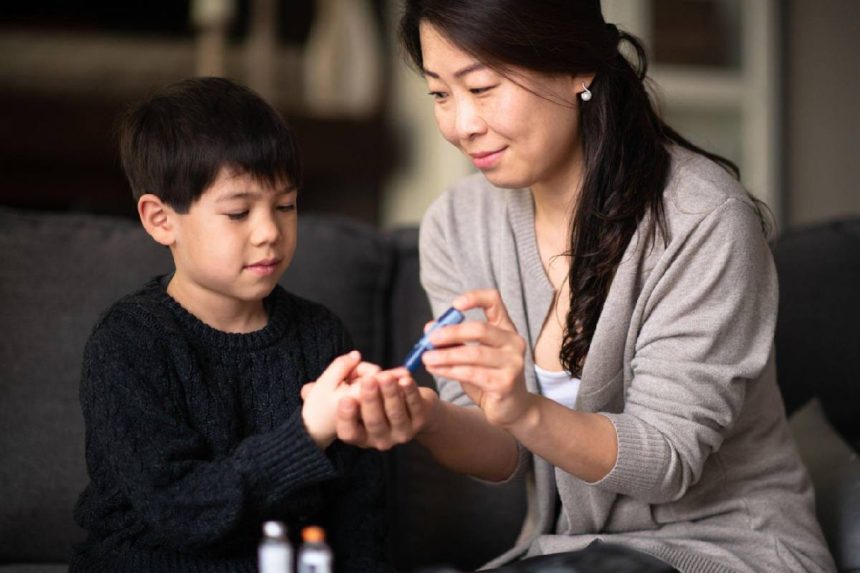
- Learn how to give shots and how to use insulin pumps and learn how to check your child’s blood sugar level and interpret the results.
Type 2 Diabetes
On the other small hand, type 2 diabetes can be prevented. This is common with kids who are overweight, obese and have a sedentary lifestyle. More children and teenagers are being diagnosed with this type 2 diabetes.
However, there are simple steps you can do to prevent and reduce your child’s risk of having type 2 diabetes:
- Healthy diet – Encourage your child to eat low-fat, nutrient-rich foods such as fruits and vegetables. Try to incorporate whole-grain cereals, bread, fruits, and vegetables into your child’s diet. This will keep their body healthy and strong.
- Limit your child’s consumption of sugary foods and beverages – sodas, juices, candies, and cake contribute to excessive weight gain, and as much as possible, we want our child to stay healthy so let’s keep them off from sugary foods.
- Encourage your kid to be physically active – limit the amount of time your child spends on sedentary activities such as watching television and playing video/computer games. Instead, encourage them to play outside or participate in sports. This will diminution the risk of weight gain and will help with your healthy diet meal plan.
It is imperative for a growing kid to get enough calories and nutrients for a healthy body and development. Excessive amounts of calories can lead to weight gain. That is why it is important that you watch your child’s diet and put the right portion of food on their plate.
Balance out the foods that you will give them and keep them healthy and active.
Having a proper diet and encouraging them to be active can help a lot in preventing them from having type 2 [diabetes]. It is also important to see a health professional know if your child needs medication, treatment, and what activities can your child do to help them improve their health.
Conclusion
DM1 is a disease that cannot prevent, but parents should be aware of its early signs and symptoms to make an early diagnosis and avoid serious complications. With proper care, professional guidance, and early diagnosis, it is possible to live with the disease healthily.